Latest News
The Future of Commercial Office Space (Cushman & Wakefield). Concerns exist about the future of commercial office space. There is no denying that the work from home trend is real and the impacts will be felt in the short and long term. A report from Cushman & Wakefield examining the global impacts of the pandemic on commercial real estate predicts office leasing will be significantly affected for many years with increasing vacancies and decreasing rents in many parts of the world. The highest level of vacancies will occur in the U.S., Canada, and European countries at a net negative level of over 200 million square feet. Even prior to the pandemic, businesses were reducing their footprint in the west, but the significant job losses and work from home (WFH) trend has and will hit the leasing market hard for quite some time. A net 215 million square feet of office vacancy will have been lost due to the pandemic. Global office vacancy will rise from 10.9% pre-COVID to 15.6% by Q2 2022. Office leasing is expected to remain below pre-COVID levels until 2025.
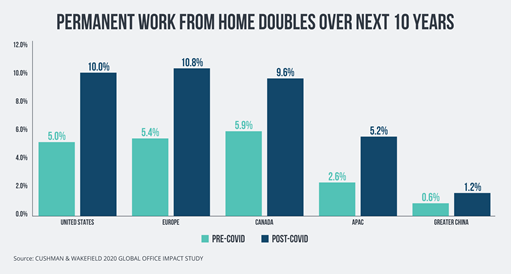
CIOs Accelerating Digital Transformation for Future of Work (CIO). Work from home is now more than a six-month-old norm for organizations across the globe. The pandemic led CIOs and IT teams across industries—irrespective of sizes—to adopt the new style of work and quickly shift their teams to virtual environments. This transformation required investment in PCs, services, and infrastructure to support the data and work happening. After the initial shift to facilitate remote working, businesses are now shifting from doing it ‘light’ to ‘right’ – where productivity, collaboration, and security have become the key pillars of the connected workforce experience. Post COVID-19, remote working is expected to increase by 20% across all sectors irrespective of sizes which will lead to increasing demand for more IT infrastructure around 5G, AI, and processing power.
State Economic Performance
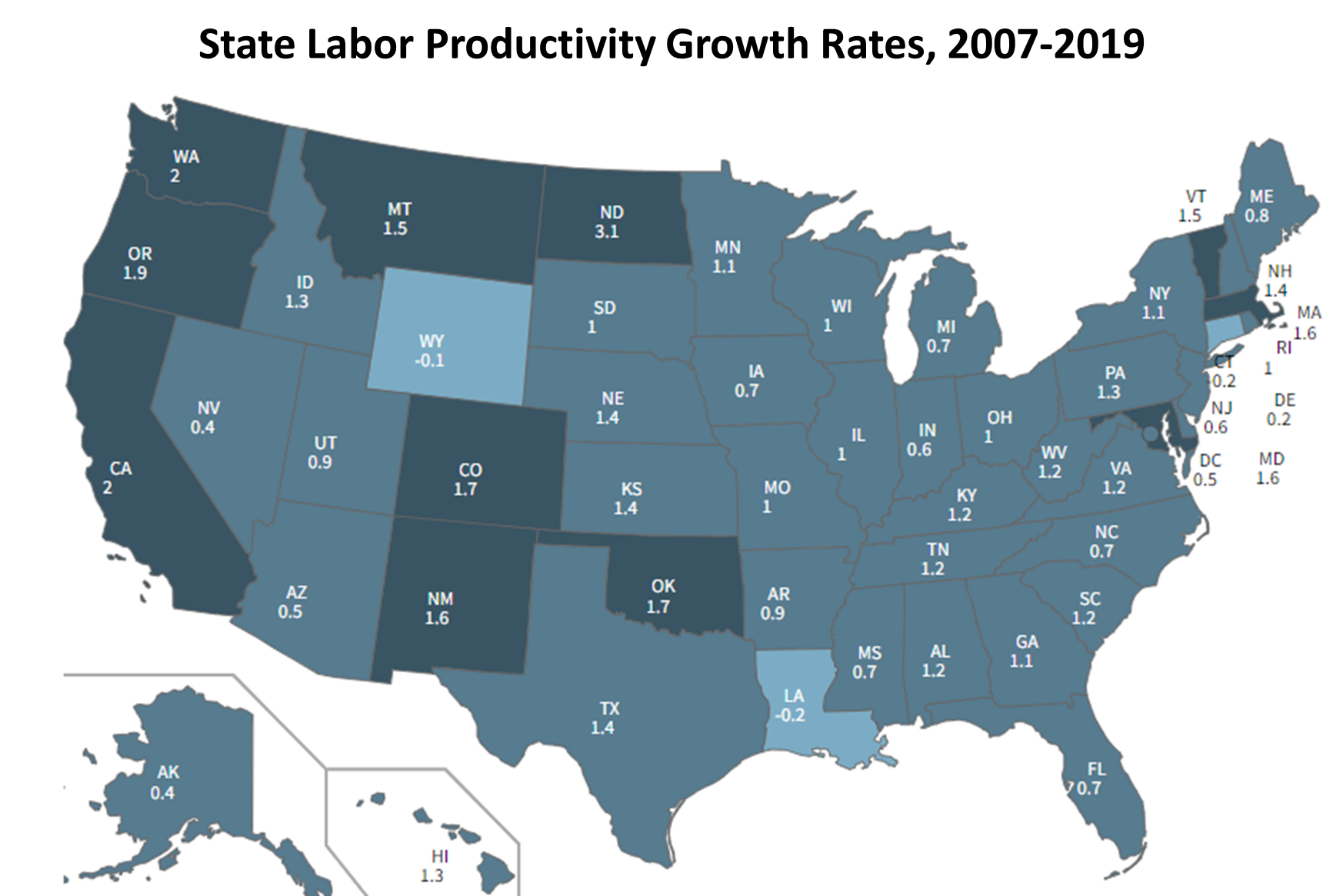
BLS Measures State Productivity (Bureau of Labor Statistics). Labor productivity is measured as the difference between the percentage growth in output and the percentage growth in hours worked. From 2007 to 2019, national productivity increased at an average annual rate of 1.2 percent. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) now publishes state-level labor productivity and cost measures for the private nonfarm sector, including output per hour, output, hours, unit labor costs, hourly compensation, and real hourly compensation. By analyzing state-level labor productivity measures, data users can learn more about regional business cycles, the persistence of regional income inequality, and which states are driving national productivity trends. Based on the BLS measure, North Dakota, California, and Washington are among the states contributing the most to national labor productivity growth.
* Economic Outlook *
We’re Recovering to a Different Economy
The Covid-19 pandemic brought the economy to a screeching halt, and while it has started its road to recovery, the economy we knew is probably a thing of the past, said Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell at the European Central Bank’s Forum on Central Banking on November 12, 2020. The pandemic has accelerated existing trends in the economy and society, including the increasing use of technology, telework and automation. This will have lasting effects on how people live and work. Even after the unemployment rate goes down and with a vaccine, there is a substantial group of workers who are going to need support finding their way in the post-pandemic economy. Lower-paid workers, as well as those in jobs requiring face-to-face interactions, such as retail or restaurant workers, will shoulder most of the burden of this shift. These groups are heavily skewed towards women and minorities.
* * *
Topics and Trends
Industry Watch
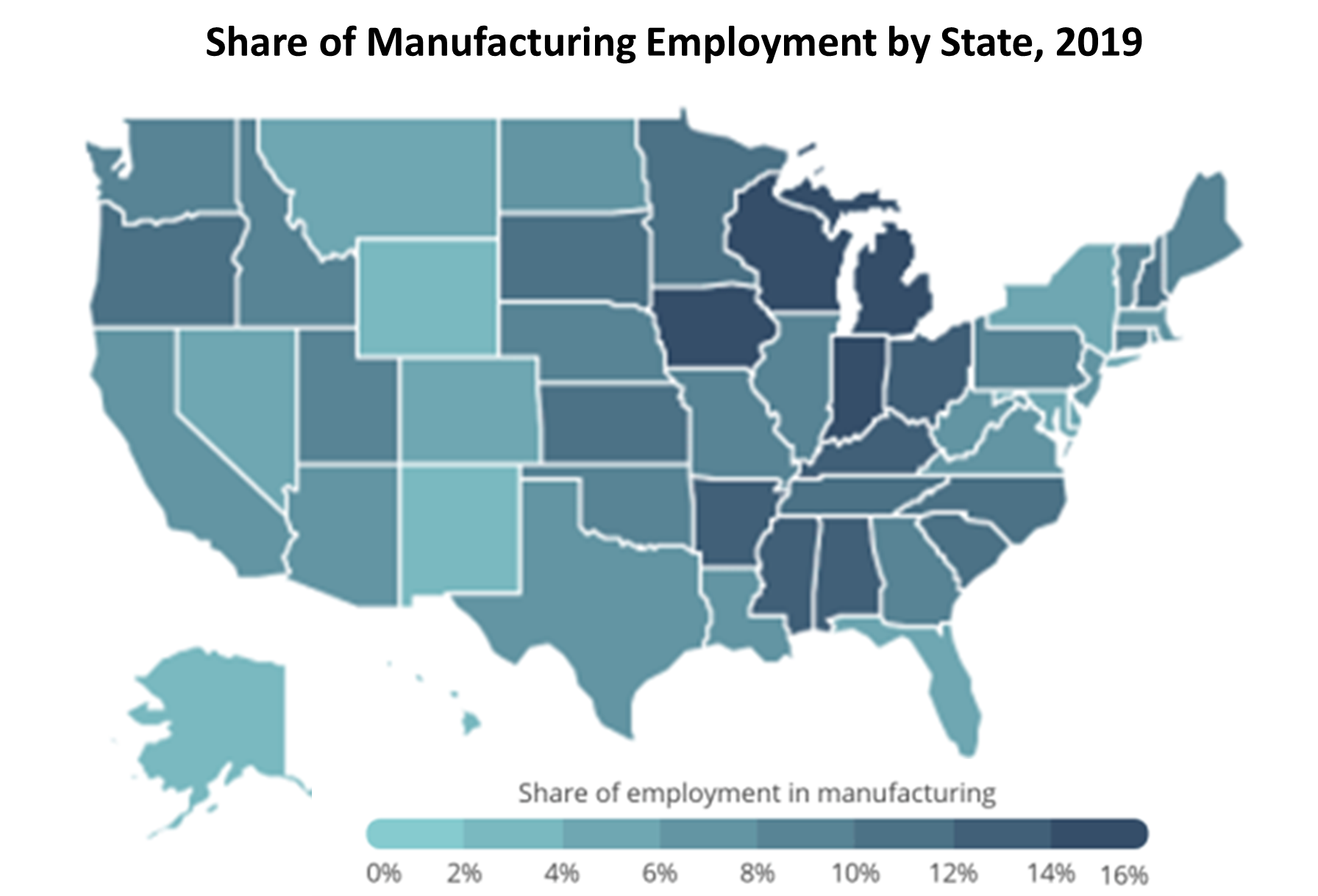
States and Cities with Most Manufacturing Jobs (Smartest Dollar). Indiana, Wisconsin, Iowa, Michigan, and Alabama have the largest percentages of their employment in manufacturing. At over twice the national average, the Grand Rapids metro area has the largest share of manufacturing employment among cities. However, manufacturing employment in the U.S. has been on the decline for decades. According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, manufacturing accounted for more than 13 percent of the U.S. nonfarm workforce in 1999, or 17.3 million jobs. Today, just 8.5 percent of workers were employed in the manufacturing sector, totaling less than 13 million jobs. While manufacturing jobs have declined, manufacturing output—measured as the value of goods and services produced—has steadily increased. In fact, labor productivity for U.S. manufacturing is 2.5 times greater than in past decades due to advances in machinery, increased worker skill, and improved industrial processes.
Trade/Tariffs
Asia-Pacific Signs World’s Biggest Trade Deal (NPR). Fifteen Asia-Pacific economies signed on to what could become the world’s largest free trade agreement, covering nearly a third of the global population and about 30% of its global gross domestic product. The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), backed by China and also including Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand and the 10 Southeast Asian nations, will progressively lower tariffs and aims to counter protectionism, boost investment, and allow freer movement of goods within the region. RCEP was signed in November at the four-day ASEAN summit in Hanoi. However, critics note the deal lacks provisions for protecting workers and the environment and will hurt smallholder farmers and businesses at a time when they are already suffering from the pandemic. Last year, India pulled out of RCEP, citing differences over tariffs and other barriers, and after protests by farmers who feared a flood of cheaper imports from countries such as China, Australia, and New Zealand.
Opportunity Zones
The 2020 Year in Review for Opportunity Zones (Motley Fool). Opportunity zones have been one of the most bipartisan pieces of legislation to pass the U.S. Congress in recent years. But as with much of 2020, the arrival of a global pandemic changed many investment plans. Hotel and office projects began to lose their appeal, and funds began to look outside big cities to other markets. President-elect Joe Biden has said he will reform the Opportunity Zone Program. His plan includes incentivizing funds to partner with local organizations to create a community benefit program for each investment. He also wants the Department of Treasury to ensure opportunity zone tax benefits are only allowed when there are clear benefits to the community. The bipartisan Improving and Reinstating the Monitoring, Prevention, Accountability, Certification, and Transparency Provisions of Opportunity Zones (IMPACT) Act emphasizes community benefits. There are also several pieces of legislation before the House and Senate that address how opportunity zones funds handle reporting. The Opportunity Zone Accountability and Transparency Act (H.R. 5011) and the Opportunity Zone Reporting and Reform Act (S. 2787) both look at how projects are tracked. To view the Final Regulations on Opportunity Zones issued by the U.S. Treasury Department and IRS, click here.
Home Prices Up but Rising Slower in Opportunity Zones (Attom Data Solutions). Housing markets in Opportunity Zones continue improving, even with the Coronavirus pandemic spread. Median home prices increased in 74 percent of opportunity zones year over year, according to Attom’s third quarter 2020 report. Home prices rose by more than 10 percent in over half of the zones. However, the gains still fell below the pace for other areas in the U.S., where about 75 percent saw prices increase by more than 10 percent year over year. The differences potentially reflect the pandemic generally hit hardest in lower-income communities that include most of the zones targeted for tax breaks designed to spur redevelopment. States with the largest percentage of zones that had annual median price increases during the third quarter of 2020 included Washington (median prices up in 88 percent of zones), Missouri (88 percent), Arizona (86 percent), Ohio (83 percent) and Rhode Island (82 percent). For more information on Opportunity Zones, CDFA has extensive resources available, click here.
The Opportunity Zones program provides a tax incentive for investors to re-invest their unrealized capital gains into Opportunity Funds that are dedicated to investing into Opportunity Zones designated by the chief executives of every U.S. state and territory. Treasury has certified more than 8,700 census tracts as Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZs) across all states, territories, and the District of Columbia. For a map of all designated QOZs, click here.
Inclusive Growth
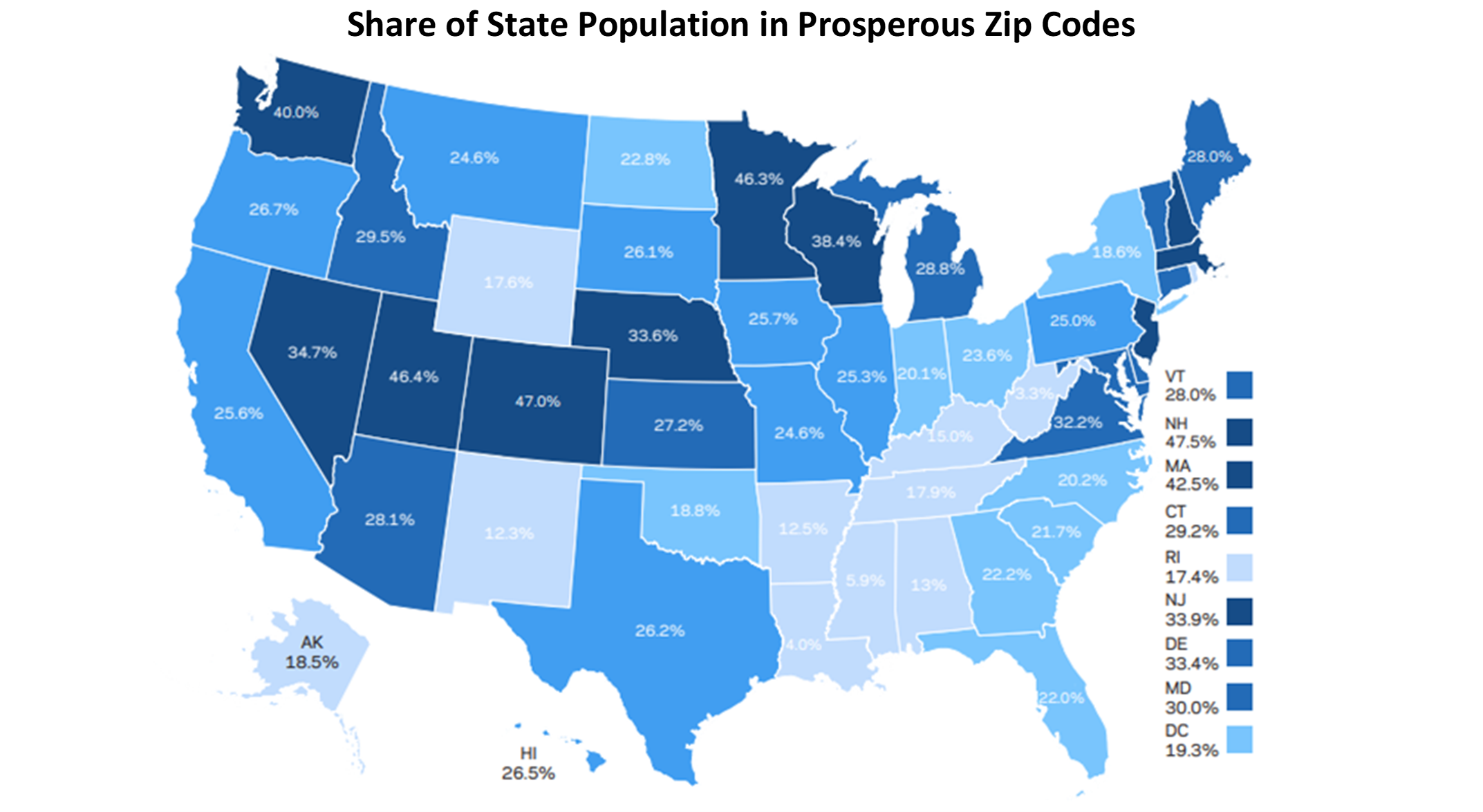
More Americans Now Live in Prosperous Areas (Economic Innovation Group). The Distressed Communities Index (DCI) sorts U.S. communities based on seven economic indicators and five categories of well-being: prosperous, comfortable, mid-tier, at risk, and distressed. A plurality of Americans (82.4 million) lives in prosperous zip codes and the share of the U.S. population residing in economically distressed zip codes fell from 18 percent in 2000 to 16 percent in 2018. Prosperous zip codes also gained 8.7 million jobs between 2000 and 2018, generating nearly 62 percent of total U.S. job growth over the period. Meanwhile, zip codes that were distressed lost jobs. New Hampshire leads the nation with 47.5 percent of its population living in prosperous zip codes and just 4.1 percent in distressed. California had the largest number of people living in prosperous zips, 10 million. High population states and communities in the Northwest have experienced the greatest increase in standing since 2000.
Innovation
Demand for Sustainable Aviation Fuel Drives Innovation (Research and Markets). Stringent regulations regarding sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is boosting the competition among aviation fuel manufacturers which is also positively impacting the overall growth of the global aviation fuel market. Various biofuels that can significantly reduce carbon emissions for aircraft offers lucrative opportunities for the growth of the aviation fuel industry. United Airlines was the first U.S. airline to begin the use of SAF for regularly scheduled flights. In 2019, Boeing announced that the company will be offering airlines and operators the option of powering their new commercial jet with biofuel for return flights. The company’s initiative aims to drive down emissions by up to 80 percent and protect the environment. Many governments are also focusing on the use of sustainable aviation fuel for military aircraft which will also drive overall market growth.
Infrastructure
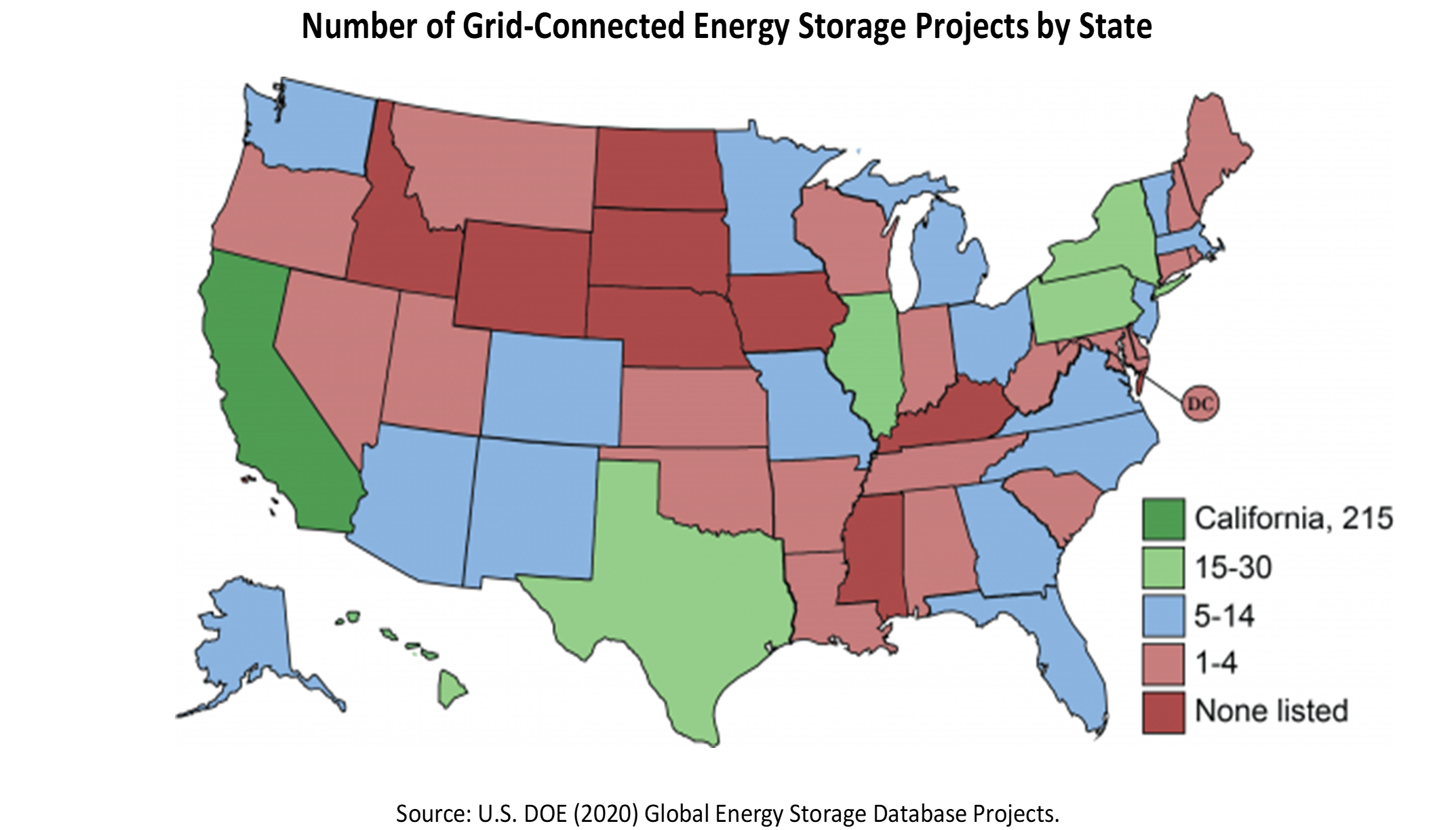
The Growing Role of Energy Storage (National Conference of State Legislatures). States have been ramping up clean energy generation. Much of this growth has been driven by state initiatives, such as financial incentives and renewable portfolio standards, coupled with the declining costs of renewable energy technologies. Many states see clean energy generation as the key to decarbonizing both the transportation and power sectors, together responsible for 55% of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. – and as an economic development opportunity. With these efforts, energy storage technologies have emerged as a critical infrastructure component to maximize the benefits of clean energy technologies. There are several types of energy storage technologies in use today, with pumped-hydro (94% of storage total) providing the most storage capacity and battery storage (6% of total) being the fastest-growing. The U.S. is among the leaders in developing and deploying energy storage infrastructure, with 40 percent of the 1,366 “renewable plus storage” projects either operational or under construction globally. For the most recent U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet, click here.
Deal Makers
Incentives in Action
* SEDE Incentives Series Report *
A New Approach to the But-For Question
Assessing the importance of incentives in influencing corporate investments is fraught with uncertainty. Since incentives are just one factor among many influencing investment decisions, there are good reasons to re-think how we have come to use the term “but for” when we talk about incentives. This paper suggests that, instead of an all-or-nothing binary approach, the effect of incentives on investment decisions should be considered as a probability between 0 and 100% and offers a methodology for estimation.
Nevada Knowledge Fund Project Promotes SBIR Success (Nevada GOED). With Knowledge Fund support, the Nevada Governor’s Office of Economic Development (GOED) has expanded a University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) program which helps technology entrepreneurs earn federal SBIR and STTR grant funding to southern Nevada at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV). The Knowledge Fund, administered by GOED, supports projects at UNLV, UNR, and the Desert Research Institute (DRI) that advance industry innovation in the state. The cornerstones of UNR’s Sierra Accelerator for Growth and Entrepreneurship (SAGE) program are mentorship and technical support. SAGE begins by helping determine if an idea or business qualifies for the SBIR and STTR programs. It then helps participants determine the right agency to apply to, map a strategy, write the best possible proposal, and navigate the federal grant submission system. GOED wants to expand the reach of the successful SAGE North program to create a statewide SBIR/STTR support structure for small business innovation.
Arizona Trains Students for Cloud Careers (Arizona ACA). The Arizona Commerce Authority (ACA) with the support of Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) announced a statewide initiative to increase access to cloud computing education in schools across Arizona. This initiative aims to train and certify 5,000 students for entry-level cloud computing careers by June 2022. Job postings data revealed a significant skills gap in Arizona for positions requiring cloud computing skills, with many of the jobs specifically seeking AWS skills. The ACA will work with Arizona secondary and post-secondary schools to enable the AWS Academy and AWS Educate programs to integrate cloud computing education into classrooms using content mapped to in-demand technical careers. AWS Academy provides no-cost, ready-to-teach, cloud computing curriculum that prepares students for industry-recognized AWS Certifications, including AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solution Architect – Associate, and AWS Certified Developer – Associate.
New Growth Opportunities
The Future of Food: Meatless? (McKinsey & Company). Plant-based “meat” is all the rage. Companies big and small are investing in alternative proteins, expecting continued strong growth. History has shown that people are willing to shift their diet. Forty years ago, we ate 90 pounds of beef per person; now we eat 60. Chicken consumption has increased from 40 to 90 pounds. Impossible Foods, headquartered in Silicon Valley, is a leader in developing alternative protein products. CFO David Lee notes: The company’s Impossible burger was never designed to compete with the health benefits of broccoli. It was designed to compete in the $1.7 trillion global meat and dairy market in which meat eaters want to eat meat not just every week but at every meal. With the Impossible burger consumers are forgoing the cholesterol with 10 to 20 percent fewer calories. Innovation will continue to power the alternative protein market. Anything the meat eater can imagine will eventually be launched. Impossible Foods, for example, creates 100 prototypes a week, such as plant-based pork, chicken noodle soup, and fish risotto. It also has platforms to develop whole cut products — steak, chicken breast, whole fish filets.
Talent Development/Attraction
National Apprenticeship Week Held (U.S. Department of Labor). National Apprenticeship Week was held November 8-14, 2020 as a nationwide celebration that brings together business leaders, career seekers, labor, educational institutions, and other critical partners to demonstrate their support for apprenticeship programs. It also provides apprenticeship sponsors with the opportunity to showcase their programs, facilities, and apprentices in their community. There are five key components that differentiate apprenticeships from other types of workplace training programs. These include pay, both work-based and classroom learning, mentorship, and earning credentials. Apprenticeship.gov maintained by the U.S. Department of Labor is a one-stop resource to connect career seekers, employers, and education partners with apprenticeship information and opportunities.

Employment, Earnings, and Occupations of Post-9/11 Veterans (U.S. Census Bureau). As the most recent and youngest veteran cohort, Post-9/11 veterans represent a large and growing segment of the veteran population. A new report from Census shows this group of veterans are more likely to be employed and earn more than nonveterans. Using American Community Survey (ACS) data, the study shows the median earnings for a Post-9/11 veteran is nearly $11,000 more per year than a nonveteran ($46,000 compared with $35,000). These veterans were more likely to work in protective services; installation, maintenance, and repair; transportation; computer and mathematical; architecture and engineering; and business and financial operations occupations.
* * *
SEDE Network Updates
* Check out the SEDE Website *
The SEDE Network engages in regular activities and events throughout the year. You can stay up to date on all these activities via the SEDE Network website. The site includes a collection of websites and other resources used by states to address the Coronavirus Challenge.

Click the link above and check it out!
* * *
The SEDE Network Steering Committee includes: Stefan Pryor (RI), Chair; Val Hale (UT), Vice Chair; Julie Anderson (AK); Mike Preston (AR); Sandra Watson (AZ); Kurt Foreman (DE); Don Pierson (LA); Kelly Schulz (MD); Kevin McKinnon (MN); Chris Chung (NC); Alicia Keyes (NM); Michael Brown (NV); Andrew Deye (OH); Dennis Davin (PA); Manuel Laboy Rivera (PR); Jennifer Fletcher (SC); Adriana Cruz (TX); Joan Goldstein (VT); Mike Graney (WV).
For further questions on the content in this Bulletin or for information on the SEDE Network contact Marty Romitti, CREC Senior Vice President, at mromitti@crec.net