
State Economic Development Bulletin
Headlines
Economic Performance
The U.S. Economy Added 311,000 Jobs in February, Outpacing Expectations (CNN)
February’s Hot Data Releases (Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve)
Inflation Gauge Increased 0.4% In February (CNBC)
Economic Outlook
Debt Default Would Cripple U.S. Economy, New Analysis Warns (New York Times)
Pace of GDP Growth, Disinflation Key in U.S. Economic Outlook (St. Louis Federal Reserve)
SEDE News
SEDE Member Spotlight: Kurt Foreman
SEDE Winter Meeting Summary
Trade
Treasury Targets Sanctions Evasion Network Moving Billions for Iranian Regime (U.S. Treasury)
U.S. Trade Deficit Widens Moderately in January (Reuters)
New U.S. Trade Controls on Russia Mark One Year of War in Ukraine (Hughes Hubbard & Reed)
U.S. Seeks Cooperation with Brazil Amid Ukraine Tensions (Miami Herald)
Industry Trends
U.S. Government Steps in to Make SVB Depositors Whole (CNBC)
Signature Bank’s Collapse Spells Trouble for Cryptocurrency Industry (Washington Post)
U.S. Manufacturing Growth Outpaces the Rest of the World (Axios)
U.S. Announces $6 Billion in Grants to Decarbonize Heavy Industry (Reuters)
Workforce
Who’s Not Working? Understanding The U.S.’s Aging Workforce (Minneapolis Federal Reserve)
Number Of Women in The Workforce Tops Pre-Pandemic Levels for First Time (Axios)
Finance And Incentives
Solar Panel Company Establishing First U.S. Manufacturing Operations in SC (ABC 25 Columbia)
Clean Drinking Water: Oregon to receive $18.9 Million (The Chronicle)
Volkswagen’s Scout to Build $2 Billion Plant In South Carolina (Reuters)
Ford Is Building a $3.5 Billion EV Battery Plant in Michigan (Thomas Net)
Panasonic Will Build Plant in Kansas (Fox 23)
Siemens Mobility Selects Davidson County for Major East Coast Manufacturing Center (NC Governor)
Economic Performance
The U.S. Economy Added 311,000 Jobs in February, Outpacing Expectations (CNN) The U.S. economy added 311,000 jobs in February, according to the latest monthly employment snapshot from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, that is a pullback from the blockbuster January jobs report, when a revised 504,000 positions were added, but shows the labor market is still emitting plenty of heat. February’s modest net job gains surpassed economists’ estimates of 205,000 jobs added. While the report is a strong one, that’s actually bad news in the broader context of the Federal Reserve’s campaign to curb high inflation, said PNC Financial Services chief economist Gus Faucher. “It’s much hotter than the economy can run, and so this means the Fed is going to have to continue to hike interest rates,” he told CNN. “And that makes a recession more likely.”
February’s Hot Data Releases (Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve) “Last month we received a barrage of data that has challenged my view in January that the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) was making significant progress in moderating economic activity and reducing inflation. Since the end of January, financial market participants have revised their outlooks in a way that has led them to mark up their expectations for the federal funds rate at the end of 2023 by about a half percentage point. Although inflation has been coming down since the middle of last year, the recent data indicates that we haven’t made as much progress as we thought. That assessment goes for both overall inflation, and “core” inflation, which strips out volatile energy and food prices and is a good guide to future price increases. And this holds for both CPI and PCE measures of inflation. Core CPI inflation over the last three months of 2022 was revised up from 3.1 percent (at an annual rate) to now be 4.3 percent.”
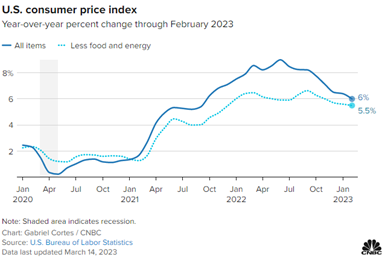
Inflation Gauge Increased 0.4% In February (CNBC) Inflation rose in February but was in line with expectations, likely keeping the Federal Reserve on track for another interest rate hike next week despite recent banking industry turmoil. The consumer price index increased 0.4% for the month, putting the annual inflation rate at 6%, the Labor Department reported March 14th. Both readings were exactly in line with Dow Jones estimates. Excluding volatile food and energy prices, core CPI rose 0.5% in February and 5.5% on a 12-month basis. The monthly reading was slightly ahead of the 0.4% estimate, but the annual level was in line.
Economic Outlook
Debt Default Would Cripple U.S. Economy, New Analysis Warns (New York Times) The U.S. economy could quickly shed a million jobs and fall into recession if lawmakers fail to raise the nation’s borrowing limit before the federal government exhausts its ability to pay its bills on time, the chief economist of Moody’s Analytics, Mark Zandi, warned a Senate panel on March 7th. The damage could spiral to seven million jobs lost and a 2008-style financial crisis in the event of a prolonged breach of the debt limit, Mr. Zandi and his colleagues Cristian Deritis and Bernard Yaros wrote in an analysis prepared for the Senate Banking Committee’s Subcommittee on Economic Policy. Mr. Zandi said he favored eliminating the statutory debt limit entirely to end the threats that a potential default posed to the economy. “I just think you want to break that cycle once and for all as best you can, because it’s very counterproductive,” he said.
Pace of GDP Growth, Disinflation Key in U.S. Economic Outlook (St. Louis Federal Reserve) U.S. economic growth, as measured by real gross domestic product (GDP), downshifted markedly in 2022, slowing from a 5.7% increase in 2021 to a 0.9% increase in 2022. Although the stepdown in growth was broad-based, growth slowed the most in personal consumption expenditures and residential fixed investment. In fact, the latter declined by 19% in 2022. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) raised the federal funds rate target range by 425 basis points in 2022. These actions slowed activity in interest rate-sensitive sectors like housing, but also had the intended effect of slowing the rate of price inflation—though admittedly, the reversal of some temporary factors (e.g., supply-side disruptions) also mattered: Growth of the all-items (headline) consumer price index (CPI) declined from 7.2% in December 2021 to 6.4% in December 2022, while the growth of the headline personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index slowed from 6% in December 2021 to 5.3% in December 2022.
SEDE News
 SEDE Member Spotlight. Kurt Foreman was appointed President and CEO of Delaware Prosperity Partnership (DPP) in the spring of 2018. DPP is the public-private economic development organization that promotes the State of Delaware as a business location for companies considering new locations or expansions and to attract entrepreneurs and innovators eager to nurture and grow new ideas and ventures in a vibrant and supportive environment. DPP is a 501c3 nonprofit funded by the state and private-sector investors. Foreman’s experience includes serving in various senior roles in economic development groups throughout the United States, including in Oklahoma, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, and twice in the Washington, D.C. metro area. Foreman has served as a site selection consultant working directly with companies to help assess and choose where to locate or expand throughout the nation. He also worked as an executive recruiter with a leading global executive search firm supporting senior-level searches across many sectors. Foreman received his bachelor’s degree at Franklin & Marshall College in Lancaster, PA, and his master’s degree from Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, NC He and his wife, Julie, have four grown children and three grandchildren.
SEDE Member Spotlight. Kurt Foreman was appointed President and CEO of Delaware Prosperity Partnership (DPP) in the spring of 2018. DPP is the public-private economic development organization that promotes the State of Delaware as a business location for companies considering new locations or expansions and to attract entrepreneurs and innovators eager to nurture and grow new ideas and ventures in a vibrant and supportive environment. DPP is a 501c3 nonprofit funded by the state and private-sector investors. Foreman’s experience includes serving in various senior roles in economic development groups throughout the United States, including in Oklahoma, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, and twice in the Washington, D.C. metro area. Foreman has served as a site selection consultant working directly with companies to help assess and choose where to locate or expand throughout the nation. He also worked as an executive recruiter with a leading global executive search firm supporting senior-level searches across many sectors. Foreman received his bachelor’s degree at Franklin & Marshall College in Lancaster, PA, and his master’s degree from Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, NC He and his wife, Julie, have four grown children and three grandchildren.
SEDE Winter Meeting Summary. The State Economic Development Executives (SEDE) Network’s Winter Networking Meeting was held on February 27-28, 2023, in New Orleans, LA. The state executives discussed a variety of topics including site improvement issues, labor force challenges, housing shortages, remote work, automation, and childcare. Alejandra Castillo, EDA Assistant Secretary, attended the meeting and offered thoughts on new EDA initiatives and how states and EDA could work together to meet important economic development challenges. Mojdeh Bahar, Associate Director for Innovation and Industry Services at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), discussed several NIST programs and noted how MEP centers can be great partners to state economic development agencies.
Trade
Treasury Targets Sanctions Evasion Network Moving Billions for Iranian Regime (U.S. Treasury) On March 9, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) sanctioned 39 entities constituting a significant “shadow banking” network, one of several multi-jurisdictional illicit finance systems which grant sanctioned Iranian entities, such as Persian Gulf Petrochemical Industry Commercial Co. (PGPICC) and Triliance Petrochemical Co. Ltd. (Triliance), access to the international financial system and obfuscate their trade with foreign customers. The action was taken pursuant to Executive Order (E.O.) 13846 and follows OFAC’s February 9, 2023, designation of nine companies in Iran, Singapore, and Malaysia for their role in the production, sale, and shipment of hundreds of millions of dollars’ worth of Iranian petrochemicals and petroleum to buyers in Asia on behalf of Triliance.
U.S. Trade Deficit Widens Moderately in January (Reuters) The U.S. trade deficit widened slightly in January as export growth nearly kept pace with increases in imports. The trade deficit increased 1.6% to $68.3 billion, and data for December was revised to show the trade gap widening to $67.2 billion instead of $67.4 billion as previously reported. Economists polled by Reuters had forecast the trade deficit rising to $68.9 billion.
New U.S. Trade Controls on Russia Mark One Year of War in Ukraine (Hughes Hubbard & Reed) On February 24th, to mark the one-year anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the White House announced a new set of sanctions and related measures targeting Russia in response to its aggression in Ukraine. The U.S. actions include new rules issued by the U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (“BIS”) that significantly broaden the export controls applicable to Russia and Belarus. The updates include:
- Strengthened export controls
- Updates to the Russian and Belarusian industry sector sanctions and luxury goods sanctions
- Changes to Russia/Belarus license requirements and creation of new Iranian license requirements
- Entity list additions
- Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) sanctions
- Increased tariffs and State Department sanctions
U.S. Seeks Cooperation with Brazil Amid Ukraine Tensions (Miami Herald) The United States and Brazil can work together to address the economic effects of the Russian invasion of Ukraine on energy supply and food production, U.S. Trade Representative Katherine Tai told the Miami Herald and el Nuevo Herald in an exclusive interview on March 10th following her trip to Brazil this week. “I went to test out the theory that this is a good moment of opportunity for the United States and Brazil, especially just weeks after President Lula’s visit to Washington, D.C. The reception I received was so warm and enthusiastic that I am really delighted, and I think there will be a lot that we can do. The most concrete outcome of this first set of meetings is that my Brazilian minister counterpart [Vice President and Minister of Development, Industry, Foreign Trade and Services Geraldo Alckmin] has agreed to reconvene under the Agreement on Trade and Economic Partnership (ATEC), an agreement between the United States and Brazil.”
Industry Trends
U.S. Government Steps in to Make SVB Depositors Whole (CNBC) Banking regulators devised a plan March 12th to backstop depositors with money at Silicon Valley Bank, a critical step in stemming a feared systemic panic brought on by the collapse of the tech-focused institution. Depositors at both failed SVB and Signature Bank in New York, which was shuttered on the 12th over similar systemic contagion fears, will have full access to their deposits as part of multiple moves that officials approved over the weekend. Along with that move, the Federal Reserve also said it is creating a new Bank Term Funding Program aimed at safeguarding institutions affected by the market instability of the SVB failure. The Fed facility will offer loans of up to one year to banks, saving associations, credit unions and other institutions. Those taking advantage of the facility will be asked to pledge high-quality collateral such as Treasurys, agency debt and mortgage-backed securities. Securities will be valued at par value rather than the market value assessed at the discount window.
Signature Bank’s Collapse Spells Trouble for Cryptocurrency Industry (Washington Post) Signature Bank, a New York based financial institution with deep ties to the cryptocurrency industry, collapsed over the weekend after depositors made a run on the bank. The bank has long been an integral financial institution for the industry, hosting tools for facilitating digital transactions and counting notable crypto companies, such as the cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase, as its clients. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation took over Signature Bank, guaranteeing that clients’ deposits over the $250,000 federal limit became available March 13th. But it is unclear how the bailout impacts other parts of the bank’s operations, notably a transaction system, Signet, used to process cryptocurrency transactions.
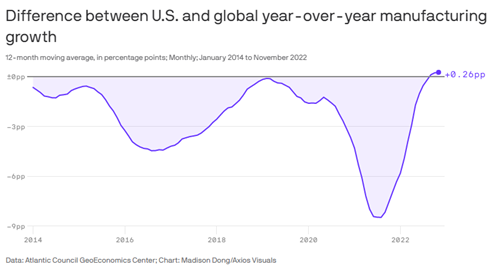 U.S. Manufacturing Growth Outpaces the Rest of the World (Axios) American manufacturing growth started outpacing the rest of the world’s growth at the end of last year — for the first time in recent memory. The reasons for the surprising flip-flop are primarily energy and Covid-related, according to the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center. The chart shows the difference between the U.S. and the world’s (excluding the U.S.) industrial production year-over-year percent change. The Atlantic Council calculations are based on data from the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
U.S. Manufacturing Growth Outpaces the Rest of the World (Axios) American manufacturing growth started outpacing the rest of the world’s growth at the end of last year — for the first time in recent memory. The reasons for the surprising flip-flop are primarily energy and Covid-related, according to the Atlantic Council GeoEconomics Center. The chart shows the difference between the U.S. and the world’s (excluding the U.S.) industrial production year-over-year percent change. The Atlantic Council calculations are based on data from the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas.
U.S. Announces $6 Billion in Grants to Decarbonize Heavy Industry (Reuters) The Biden administration said on March 8th it is directing $6 billion in funding to speed decarbonization projects in energy-hungry industries like steel, aluminum, and cement making that contribute nearly 25% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. The Industrial Demonstrations Program will provide competitive grants to technology developers, industry, universities, and others for up to 50% of the cost of projects that aim to cut emissions from industry that also includes production of chemicals, ceramics and paper, the Department of Energy (DOE) said.
Workforce
Who’s Not Working? Understanding the U.S.’s Aging Workforce (Minneapolis Federal Reserve) The American workforce has gotten older, with young people staying in school longer and older people increasingly delaying retirement. Seniors aged 65 to 69, past the standard retirement age, are more likely to have a job than teenagers. A full 32 percent of these post-retirement-age seniors have jobs, up from less than one-quarter in 2000. This isn’t just an artifact happening at the extremes. Work has become less common this century among every single age bracket under 55, while every single age bracket over 55 is more likely to work. No single factor explains this long-term shift in the U.S. workforce. While the U.S. population is getting older, the data show a changing workforce even controlling for age. Other factors include:
- Young people are more likely to be in school
- Students are less likely to work
- Older Americans are delaying retirement
Number Of Women in The Workforce Tops Pre-Pandemic Levels for First Time (Axios) The number of women in the workforce in February was higher than pre-pandemic levels for the first time, according to the latest jobs data out March 10th. The strength of women’s return to work was faster than anyone could have imagined just a few years ago when dire predictions about a “she-cession” flooded the news. 105,000 of the 311,000 jobs added in February were in the leisure and hospitality sector, where women hold most positions. Women’s labor force participation — that is, the percentage of women working or looking for work — is at 57.2%, almost back to the February 2020 participation level of 57.9%.
Finance And Incentives
Solar Panel Company Establishing First U.S. Manufacturing Operations in SC (ABC 25 Columbia) A global solar panel manufacturer announced plans to establish its first U.S. facility in Orangeburg County, South Carolina. Hounen Solar serves the clean energy market by providing solar photovoltaic panels and other electrical products worldwide. The company plans to lease a 200,720 square-foot plant and invest $33 million in operations. The expansion will create 200 new jobs.
Clean Drinking Water: Oregon to receive $18.9 Million (The Chronicle) Oregon will receive $18.9 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to address emerging contaminants like Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in drinking water. Oregon received this funding through the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Emerging Contaminants in Small or Disadvantaged Communities (EC-SDC) Grant Program that assesses and improves access to safe and clean water in small, rural, and disadvantaged communities while supporting local economies.
Volkswagen’s Scout to Build $2 Billion Plant In South Carolina (Reuters) Volkswagen’s off-road brand Scout Motors said March 3rd it would build a $2 billion manufacturing plant near Columbia, South Carolina, for trucks and SUVs. The investment could potentially create 4,000 or more permanent jobs and more than 200,000 Scout vehicles could be produced annually at the facility. Groundbreaking is planned for mid-2023 and production is projected to begin by the end of 2026. Scout, an independent U.S. company owned by Volkswagen Group, is currently evaluating the potential for outside investment.
Ford Is Building a $3.5 Billion EV Battery Plant in Michigan (Thomas Net) The latest auto brand to make waves in battery development is Ford, who recently announced plans to build an EV battery plant in its home state of Michigan. The investment amounts to $3.5 billion, and Ford says it will produce lithium-iron-phosphate, or LFP batteries, with the help of tech partner CATL. Ford says the plant should create around 2,500 jobs in Marshall, Michigan, and will pay $20 to $50 an hour. The company hopes to be online by 2026.
Panasonic Will Build Plant in Kansas (Fox 23) Panasonic has chosen to build its new electric car battery factory in Kansas, edging out Oklahoma for the financial opportunity worth several billion dollars. Politicians in Kansas and Oklahoma have been courting the company for months. Oklahoma Governor Kevin Stitt signed House Bill 4455 into law in April. The Lead Act provides nearly $700 million dollars in financial incentives to any company that meets certain requirements when building a facility in Oklahoma. Panasonic builds batteries for Tesla vehicles.
Siemens Mobility Selects Davidson County for Major East Coast Manufacturing Center (NC Governor) Siemens Mobility, Inc., the global manufacturer of rail transportation vehicles and control systems, will build a major advanced manufacturing and rail services center in Davidson County, creating 506 jobs. Siemens Mobility’s advanced manufacturing center in North Carolina will involve multiple buildings on the 200-acre site, which will also feature more than 11,000 feet of rail track. The company will manufacture passenger rail vehicles at the Lexington facility, allowing it to better serve its East Coast customers while meeting growing demand for its products.
The State Economic Development Executives (SEDE) Network engages in regular events throughout the year. State Economic Development.org lists these activities and offers an interactive forum for discussion among peers. The website is currently undergoing some minor reorganization, including adding resources on how state and local economic development districts can align strategies and collaborate on activities.
The SEDE Steering Committee includes: Sandra Watson (AZ), Chair; Don Pierson (LA), Vice-Chair; Mike Preston (AR); Kurt Foreman (DE); Kevin McKinnon (MN); Christopher Chung (NC); Alicia Keyes (NM); Andrew Deye (OH); Sophorn Cheang (OR); Adriana Cruz (TX); Joan Goldstein (VT); Lisa Brown (WA) and Mike Graney (WV).
Leif Olson of the Center for Regional Economic Competitiveness (CREC) led the development of this Bulletin; for questions on the content in this Bulletin or for information on the SEDE Network contact Bob Isaacson, CREC Senior Vice President.